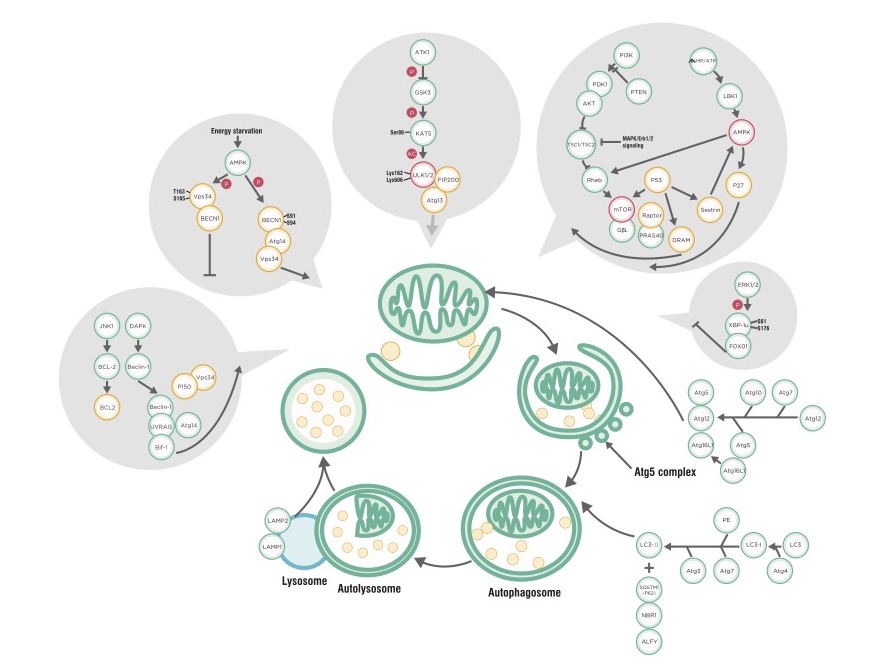
Every now and then when I get hungry, I joke that my stomach is about to digest itself. For the longest time, human science was unaware that our cells could literally eat itself (or more precisely, parts of itself) as well! First described in the 1960s by Christian de Duve (who won the Nobel Prize for discovering the lysosome), the term autophagy derives from Greek words combined to mean “self-eating” and describes a process by which the cell degrades large components and organelles in a distinct mechanism. 1-3 The phenomenon was not studied extensively until the 1990s, when Yoshinori Ohsumi performed a series of groundbreaking experiments to determine the underlying mechanisms of autophagy, an achievement for which he was awarded the 2016 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Ohsumi’s work has led to an explosion of research that has precipitated a greater understanding of the role played by cellular digestion, degradation, and recycling pathways in human health and disease.