Long-interspersed nuclear elements (LINEs) are genetic components found in higher eukaryotes. They are retrotranposons, meaning that they are transcribed into mRNA and then translated into proteins that act as a reverse transcriptase. The reverse transcriptase makes a copy of the LINE DNA which can then be integrated into the genome at a new site. The only active LINE in humans is LINE-1. It has been associated with oncogenesis and Haemophilia A, a diseased caused by insertional mutagenesis.
Scientists Identify Novel Regulator for LINE-1 Using ABclonal Antibody
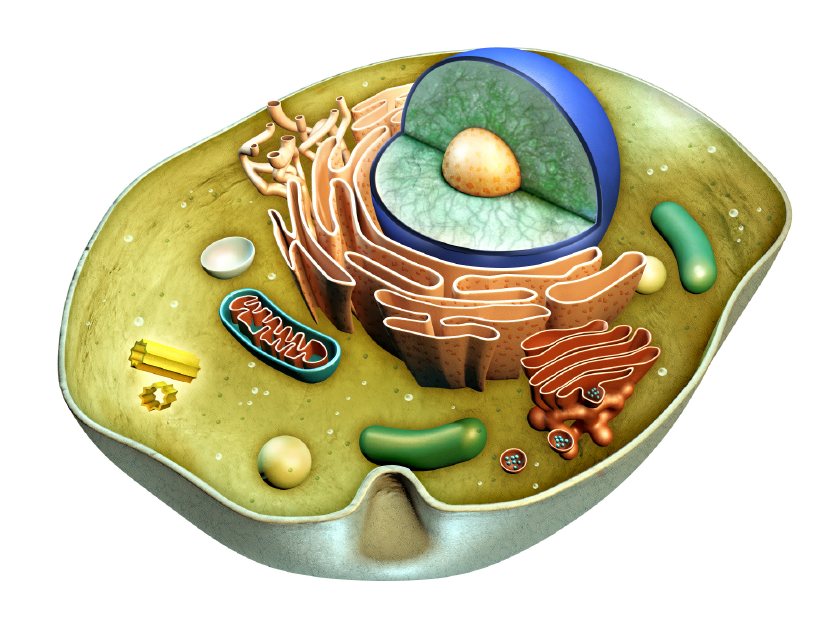
Although underappreciated, the Golgi apparatus is indispensable to normal cellular function by ensuring proteins are properly folded and sorted, and to direct diverse functions including autophagy. Disruptions to proper Golgi function can lead to many disease states, including diabetes, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease. The study of vesicular markers, including Golgi markers, is critical to our understanding of this amazing organelle's function in keeping the cell and organism healthy. Clarifying the mechanisms by which proteins are properly folded, sorted, quality controlled, and transported will prove important as more effective therapies are developed against a diverse array of human diseases.
We have previously explored the function of organelle markers USO1, GOLGA2, and GOLM1 but not how the corresponding antibodies can be applied in research. Organelle marker antibodies are common tools in cell biology research. They can be used with immunofluorescence technology to observe the morphological structure of organelles and understanding the subcellular localization of proteins. In turn, they help to explore the biological functions/role of organelle proteins in normal or disease models. These markers can also be used in Western blot (WB) experiments examining organelle extracts: as a positive control to determine whether the organelle is successfully extracted.
You can see some examples of ABclonal Technology's Golgi marker antibodies below. These are only a handful of the huge selection of targets that you can use to supplement your cutting-edge research!
Organelle marker antibodies are common tools in cell biology research. They can be used with immunofluorescence technology to observe the morphological structure of intracellular membrane-bound organelles and for understanding the subcellular localization of proteins. In turn, they help to explore the biological functions/role of organelle proteins in normal or disease models. These markers can also be used in Western blot (WB) experiments examining organelle extracts, as well as providing a positive control to determine whether the organelle is successfully extracted.
We focus today on the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) markers. The ER is a network of membrane-bound organelles that are the initial destination for proteins that are targeted for other organelles, the plasma membrane, or are to be secreted outside the cell. Proper ER function includes accepting the nascent protein as it is being translated by ribosomes, and ensuring that the protein is properly folded so it does not lead to accumulation of unusable cellular cargo. Disruptions in ER or the unfolded protein response can lead to cell death or various disease states such as cancer or neurodegenerative disorders.
ABclonal provides many antibody products for the study of ER and Golgi markers, as well as exosome markers. Please read our blog on the vesicular transport system and its role in cellular homeostasis, and check out some of our ER marker antibodies below. We are honored to be part of your journey to better understanding vesicular transport and the fight against human diseases!
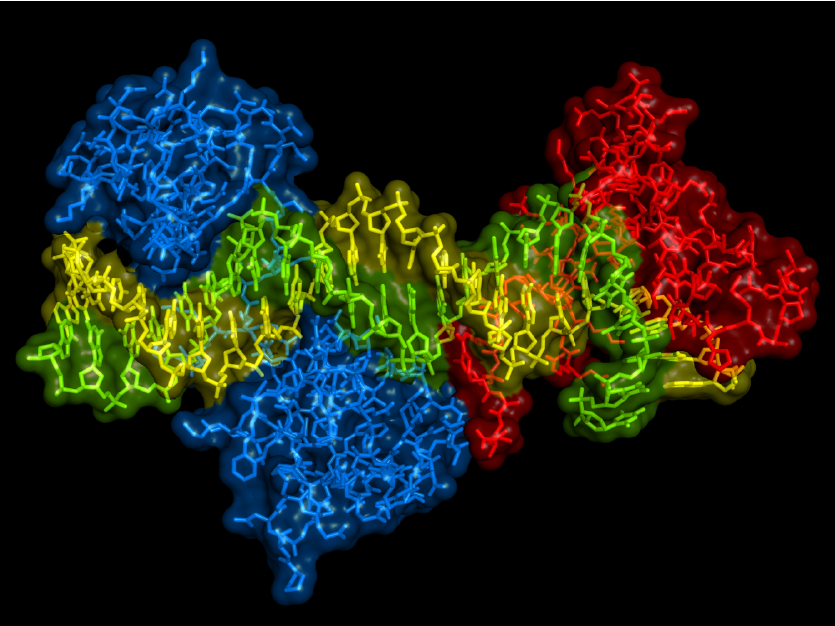
CTCF (CCCTC Binding Factor) is a highly conserved transcription factor that regulates transcriptional activation, transcriptional repression, insulator function, and imprinted control regions (ICRs).
Autophagy is a catabolic process in which autophagic lysosomes, known as autophagosomes, degrade most cytoplasmic contents, including entire organelles like damaged mitochondria in protection of the host cell and organism. Autophagy is usually activated in the absence of nutrients and is associated with many physiological and pathological processes, including growth, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, infections and tumors. Light chain 3 (LC3) is a widely recognized autophagy marker. There are three isoforms of the LC3 protein (LC3A, LC3B, and LC3C) in mammals. They undergo post-translational modifications during autophagy. The LC3 protein is first cleaved by Atg4 at its carboxy terminus immediately after synthesis to produce LC3-I, which is localized in the cytoplasm. During autophagy, LC3-I is modified and processed by a ubiquitin-like system including Atg7 and Atg3 to produce LC3-II with a molecular weight of 14 kD and localized to autophagosomes. The magnitude of the LC3-II/I ratio can be used to assess the level of autophagy.
ABclonal Technology is pleased to offer numerous antibody products to study targets within the autophagy pathway, be it the normal functions within the pathway, the autophagic cell death pathway, or disruptions to autophagy that may drive disease progression. Many of our products have been peer reviewed by satisfied customers, including those who have used them to generate quality data for scientific publications. Please see some examples of our products below, and happy experimenting!
ABclonal Technology hosted its second lunch and learn at the Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research at MIT, the second event of its lecture series. The lunch and learn, led by ABclonal’s senior principal scientist, focused on rabbit monoclonal antibody technologies, its advantages and development.