Cluster of differentiation, or CD molecules, are cell surface markers that are used for identification of cell types in pathology and other bioscience disciplines. The expression levels of CD markers may increase or decrease (or disappear altogether, at least to undetectable levels) when cells (for example, leukocytes, red blood cells, platelets, and vascular endothelial cells, etc.) differentiate into new and different lineages. Depending on the CD marker, the expression level may identify a phenotype for different segments of cells, such as when they become active or diseased. Most CD molecules are transmembrane proteins or glycoproteins, including extracellular regions that bind a ligand or opposing receptor, transmembrane regions to anchor the CD marker into the cell, and cytoplasmic regions that may confer some adaptor or catalytic function. Some CD molecules can also be "anchored" on the cell membrane by means of inositol phospholipids. A few CD molecules are carbohydrate haptens. The study of CD molecules can be used in many basic immunology research fields, such as the relationship between CD antigen structure and function, cell activation pathway, signal transduction and cell differentiation, etc. It can be used clinically for disease mechanism research, clinical diagnosis, disease prognosis, efficacy tracking and treatment, and more. CD molecules such as CD4, CD8, CD25, etc. can be used to identify populations of cells when studying samples by flow cytometry or immunofluorescence.
The Hippo signal is very conservative in evolution. It regulates organ size and tissue stability by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, and stem cell renewal. The core process of Hippo signaling is a kinase tandem process, Mst1/2 and Sav1 form a complex, phosphorylate and activate Lats1/2; Lats1/2 kinase then phosphorylates and inhibits transcriptional coactivators Yap and Taz. Yap and Taz are the most important effectors downstream of the Hippo pathway. Upon dephosphorylation, Yap and Taz translocate to the nucleus and interact with TEAD1-4 or other transcription factors (such as CTGF) to induce gene expression, thereby initiating cell proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis.
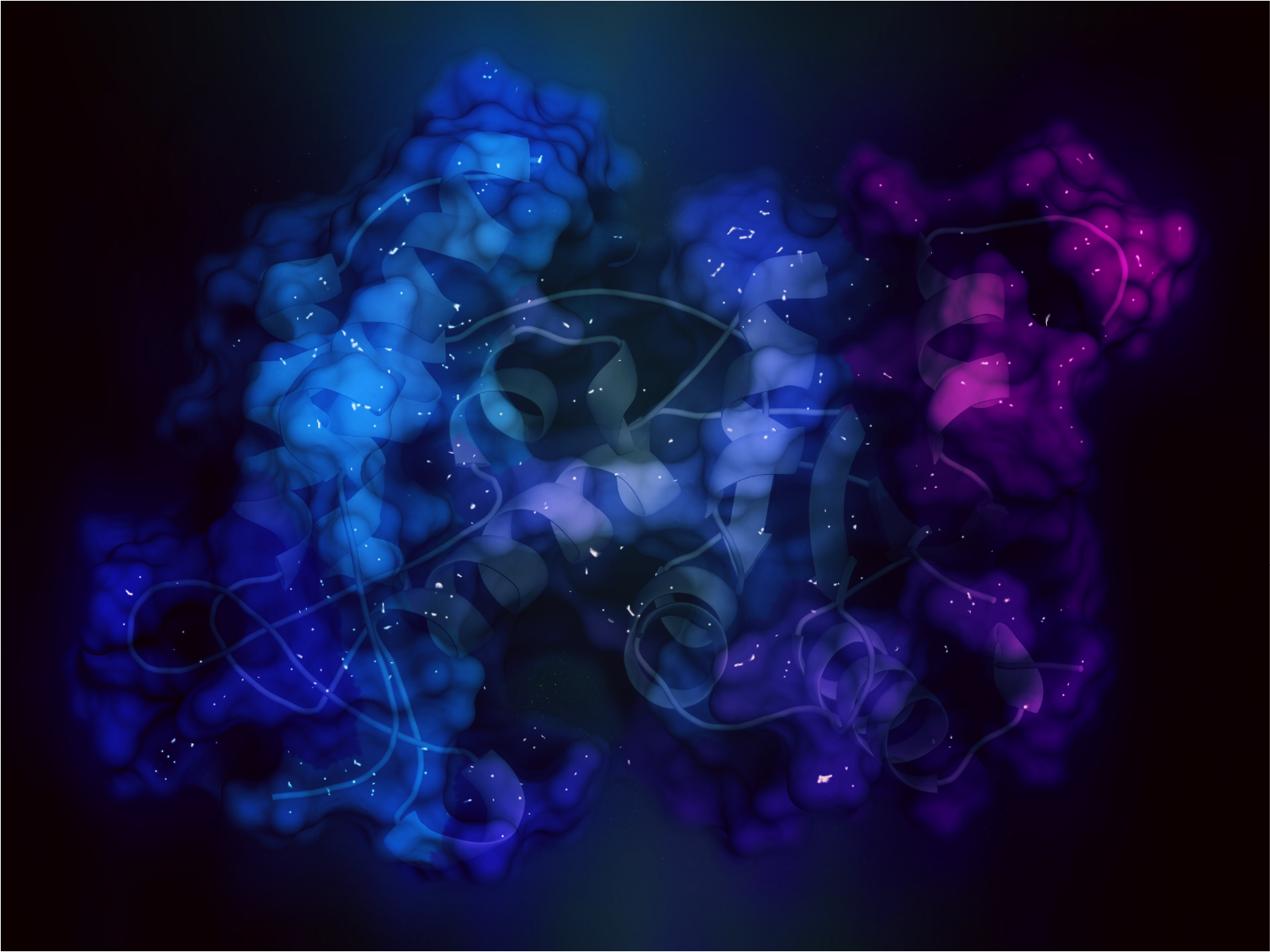
The glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, or GAPDH for short), is a multifunctional, indispensable enzyme found in all cells. The generally known function of GAPDH is to assist in carbohydrate metabolism as a key player in glycolysis, but there are studies demonstrating its role in the nucleus as well.
GAPDH is a constitutively expressed housekeeping protein, and GAPDH mRNA levels and protein levels are often used as loading controls in experiments that quantify target-specific expression changes. Recent studies have elucidated the role of GAPDH in apoptosis, gene expression through its possible activities as a transcription factor, and nuclear transport. As both a metabolic protein as well as one that might play a role in cytoskeletal reorganization, GAPDH activity is intricately tied to tumorigenesis. GAPDH may also play a role in neurodegenerative diseases such as Huntington's disease and Alzheimer's disease. Therefore, although many researchers do use GAPDH as a control, this protein needs to be appreciated for its myriad other functions as well!
ABclonal Technology's GAPDH recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibody is a human-specific antibody that can be used with a high dilution ratio of 1:2560000. As a highly-stable antibody product, this means that you can perform numerous Western blotting experiments over a long period of time using a small quantity of antibody, as well as in other experiments to study the functions of GAPDH. Take advantage of this robust, cost-effective antibody product in your research today!
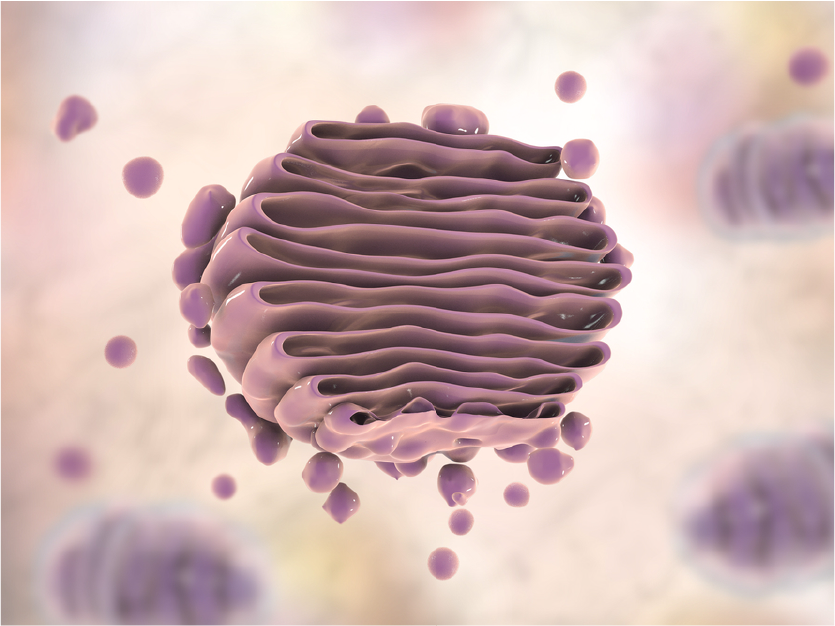
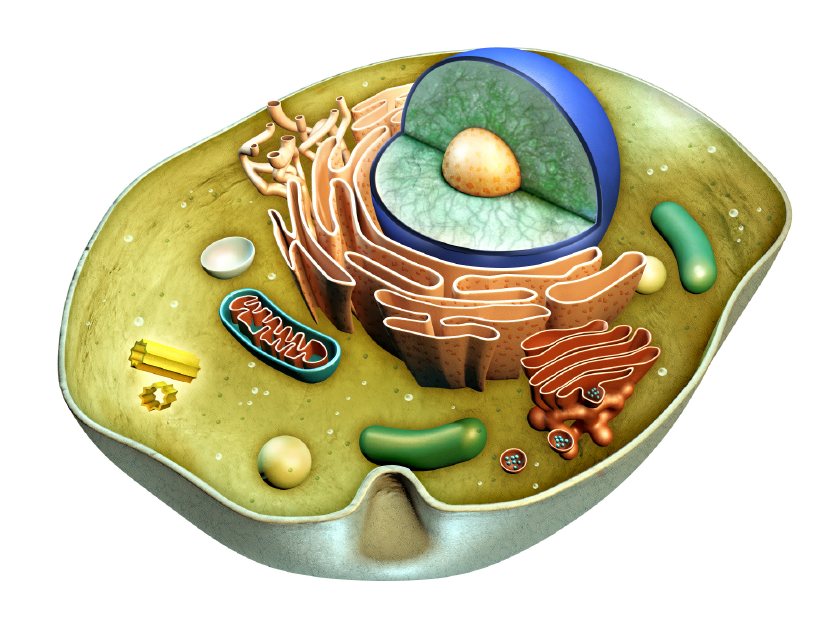
Although underappreciated, the Golgi apparatus is indispensable to normal cellular function by ensuring proteins are properly folded and sorted, and to direct diverse functions including autophagy. Disruptions to proper Golgi function can lead to many disease states, including diabetes, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease. The study of vesicular markers, including Golgi markers, is critical to our understanding of this amazing organelle's function in keeping the cell and organism healthy. Clarifying the mechanisms by which proteins are properly folded, sorted, quality controlled, and transported will prove important as more effective therapies are developed against a diverse array of human diseases.
We have previously explored the function of organelle markers USO1, GOLGA2, and GOLM1 but not how the corresponding antibodies can be applied in research. Organelle marker antibodies are common tools in cell biology research. They can be used with immunofluorescence technology to observe the morphological structure of organelles and understanding the subcellular localization of proteins. In turn, they help to explore the biological functions/role of organelle proteins in normal or disease models. These markers can also be used in Western blot (WB) experiments examining organelle extracts: as a positive control to determine whether the organelle is successfully extracted.
You can see some examples of ABclonal Technology's Golgi marker antibodies below. These are only a handful of the huge selection of targets that you can use to supplement your cutting-edge research!
Organelle marker antibodies are common tools in cell biology research. They can be used with immunofluorescence technology to observe the morphological structure of intracellular membrane-bound organelles and for understanding the subcellular localization of proteins. In turn, they help to explore the biological functions/role of organelle proteins in normal or disease models. These markers can also be used in Western blot (WB) experiments examining organelle extracts, as well as providing a positive control to determine whether the organelle is successfully extracted.
We focus today on the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) markers. The ER is a network of membrane-bound organelles that are the initial destination for proteins that are targeted for other organelles, the plasma membrane, or are to be secreted outside the cell. Proper ER function includes accepting the nascent protein as it is being translated by ribosomes, and ensuring that the protein is properly folded so it does not lead to accumulation of unusable cellular cargo. Disruptions in ER or the unfolded protein response can lead to cell death or various disease states such as cancer or neurodegenerative disorders.
ABclonal provides many antibody products for the study of ER and Golgi markers, as well as exosome markers. Please read our blog on the vesicular transport system and its role in cellular homeostasis, and check out some of our ER marker antibodies below. We are honored to be part of your journey to better understanding vesicular transport and the fight against human diseases!
CTCF (CCCTC Binding Factor) is a highly conserved transcription factor that regulates transcriptional activation, transcriptional repression, insulator function, and imprinted control regions (ICRs).